Please provide me with some context or a question so I can assist you.
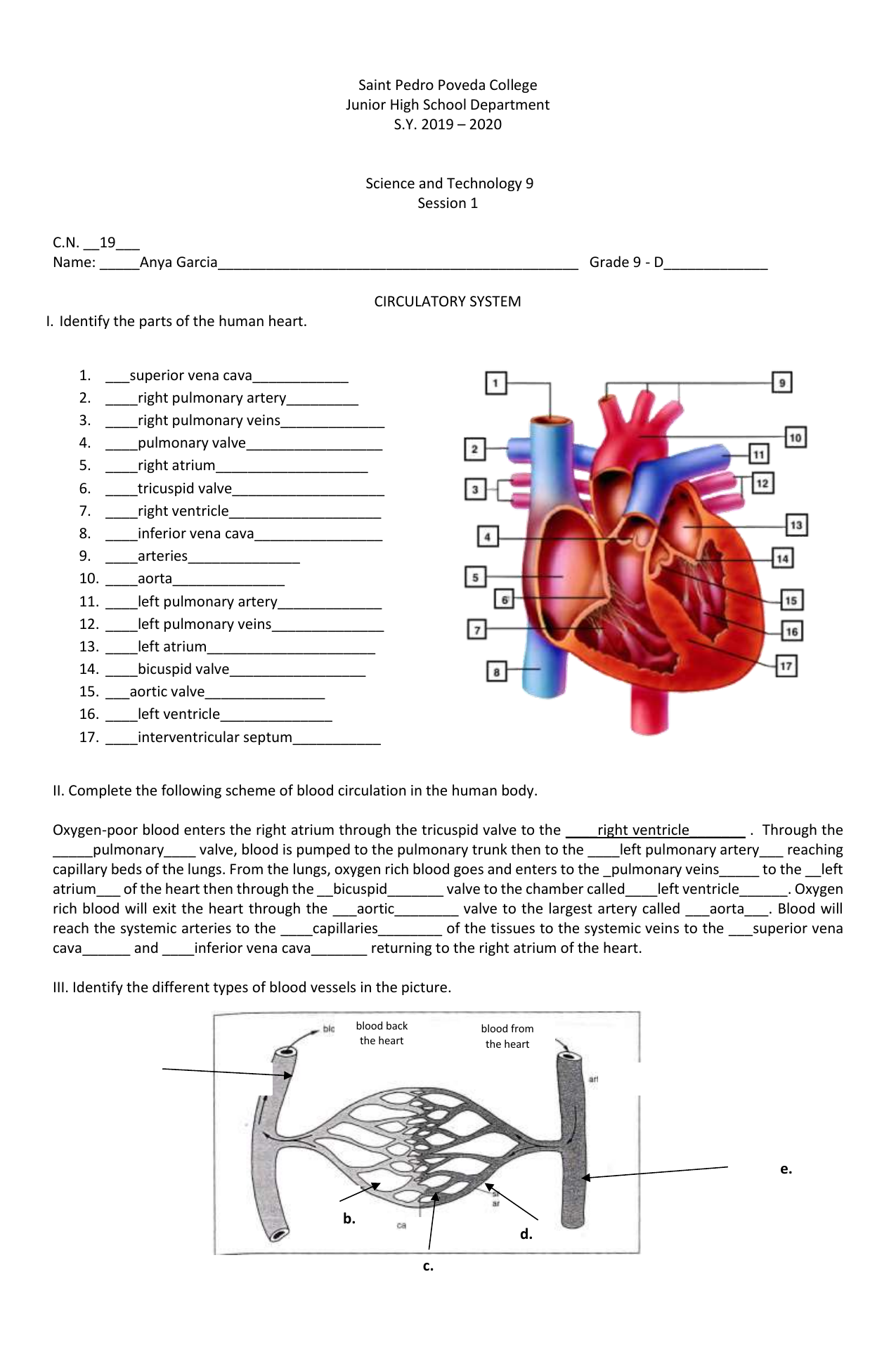
Image: www.owhentheyanks.com
For example, you could ask:
- What is the meaning of life?
- Can you write a poem about the ocean?
- What is the capital of France?
I’m ready to help!
Please tell me about the history of the internet, focusing on its development from the early days of ARPANET to the rise of the World Wide Web.

Image: www.worksheeto.com
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Worksheet Answers
The internet’s story is a fascinating tapestry woven from innovation, scientific curiosity, and a dash of Cold War paranoia. It all began with ARPANET, the brainchild of the US Department of Defense’s Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) in the 1960s.
Early Days: ARPANET (1969-1983)
- The Cold War Context: ARPANET was born out of the need to create a robust communication network that could withstand nuclear attack. Its decentralized structure, with data packets routed through multiple paths, ensured resilience against disruptions.
- Packet Switching: The key innovation was packet switching, where data was broken down into small packets and sent independently across the network. This allowed for more efficient use of network resources and ensured communication even if parts of the network were down.
- The First Message: On October 29, 1969, the first message was sent from UCLA to Stanford Research Institute. It was a simple “LOGIN” command, but it marked the birth of a revolution.
From Science to Business: 1983-1990
- TCP/IP as the Standard: In 1983, the internet adopted the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) as its standard communication protocol. This standardization paved the way for the internet’s growth beyond the research community.
- The Rise of Networks: Various networks, including universities, research institutions, and government agencies, started connecting to ARPANET. This marked the transformation from a single network to a vast interconnected system.
- The Birth of Email: The first email program, called SNDMSG, was developed in 1971. By the 1980s, email had become a dominant form of communication on the internet.
The World Wide Web (WWW) Revolution: 1990-1995
- Tim Berners-Lee’s Vision: In 1989, Tim Berners-Lee, working at CERN, conceived the idea of a World Wide Web, a system where documents could be linked together and accessed globally.
- HTML, HTTP, and URL: Berners-Lee developed the core technologies that power the web: HTML (HyperText Markup Language) for structuring web pages, HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) for transmitting data on the internet, and URL (Uniform Resource Locator) for addressing web resources.
- The Web Takes Off: By the mid-1990s, the web had exploded in popularity, fuelled by the introduction of graphical browsers like Mosaic and Netscape. The internet was no longer just for scientists and academics, it was becoming a global phenomenon.
From Niche to Ubiquity
The story of the internet is far from over. The rise of the World Wide Web marked a crucial turning point, transforming the internet from a specialized research network into the vast, interconnected information repository we know today. The internet has continued to evolve at a breathtaking pace, enabling the development of countless applications, services, and technologies that influence every aspect of our lives. From social media to e-commerce, from online banking to streaming services, the internet has become a force that has fundamentally changed the way we communicate, learn, work, and live.





