Imagine waking up to a searing pain in your chest, a tightening sensation that feels like an elephant is sitting on your chest. You break out in a cold sweat, your heart pounding a frantic rhythm against your ribs. This terrifying scenario is the stark reality of a myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack. This silent threat can strike anyone, at any time, and it demands immediate and expert medical care. As a nurse, you are the front line, the compassionate guardian who steps in to offer comfort, treatment, and hope during this critical time. This guide delves into the essential nursing care plan for patients experiencing myocardial infarction, offering a roadmap to navigate this challenging health crisis.

Image: www.vrogue.co
A myocardial infarction occurs when a blood clot blocks the flow of oxygen-rich blood to a section of the heart muscle. Deprived of oxygen, the heart tissue starts to die, leading to irreversible damage. The consequences can be devastating, ranging from long-term heart dysfunction to sudden cardiac arrest. Prompt medical intervention is crucial for minimizing damage and improving the chances of survival. This is where your role as a nurse becomes paramount. You are the key to providing the specialized care, monitoring, and support that a patient undergoing this crisis needs.
Understanding the Nursing Care Plan: A Roadmap to Recovery
The nursing care plan for a patient with myocardial infarction is a comprehensive guide designed to address the patient’s individual needs. It encompasses a multi-faceted approach, focusing on a variety of critical aspects that influence their recovery:
1. Assessing the Patient: Recognizing the Signs and Symptoms
The first step in managing a patient with myocardial infarction is to conduct a thorough assessment. This involves evaluating their vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. Pain assessment is crucial, noting its location, intensity, and character. You must also closely observe for other indicators like nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
2. Emergency Interventions: A Race Against Time
Time is of the essence when managing an acute myocardial infarction. Every second counts. You’ll need to act quickly and decisively, prioritizing the following:
- Immediate Administration of Oxygen: Supplying oxygen is a priority in order to compensate for the compromised blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG Monitoring): Monitoring the ECG is vital for identifying heart rhythm abnormalities, which can indicate further complications.
- Nitroglycerin Administration: This medication helps to dilate the blood vessels, improving blood flow to the heart.
- Morphine Administration: Morphine can be administered for pain relief and to reduce anxiety.
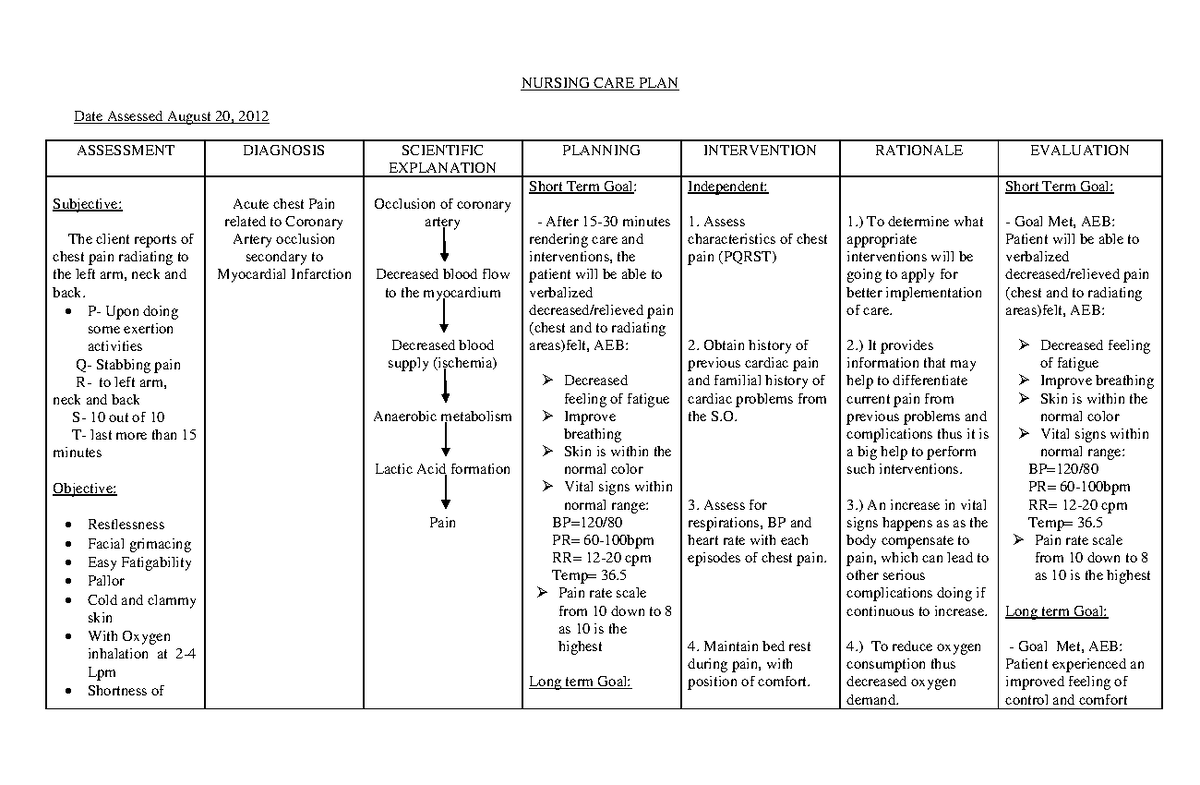
Image: www.studocu.com
3. Medication Management: The Lifeline of Recovery
You will be responsible for administering medications according to doctor’s orders. These may include:
- Antiplatelet Agents: These medications, like aspirin, help to prevent blood clots from forming.
- Beta-Blockers: Slow down the heart rate and lower blood pressure, reducing the heart’s workload.
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors: These medications help to relax blood vessels and reduce the heart’s workload.
4. Monitoring for Complications: Staying Vigilant
A myocardial infarction is a complex situation that can lead to several serious complications. You will be on high alert for signs of:
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: These are abnormal heart rhythms that can be life-threatening.
- Heart Failure: This occurs when the heart is unable to pump blood effectively.
- Cardiogenic Shock: A critical condition where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs.
5. Pain Management: Alleviating the Agony
Heart attack pain can be excruciating. It is vital to effectively manage pain and provide comfort to the patient. This may involve a combination of medications and non-pharmacological techniques, like deep breathing and relaxation exercises.
6. Promoting Rest and Comfort: A Vital Element for Healing
Patients need to rest and avoid any strenuous activity. This allows their heart to conserve energy and focus on healing. It’s essential to provide them with a calm and supportive environment.
7. Emotional Support: Being a True Companion
A heart attack is a traumatic experience. Patients may experience fear, anxiety, and depression. You will be a source of emotional support, providing empathy, reassurance, and encouragement.
8. Teaching and Empowering the Patient: Building a Durable Foundation for Health
Education is essential for helping patients manage their condition and prevent future episodes. You will be responsible for teaching them about:
- Lifestyle Modifications: This includes adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress.
- Medication Adherence: Emphasizing the importance of taking medications as prescribed.
- Follow-up Care: Instructing them on the importance of regular follow-up appointments with their doctor.
Expert Insights: A Focus on Compassionate Care
“Nurses play an indispensable role in managing patients with myocardial infarction,” emphasizes Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned cardiologist specializing in heart attack treatment. “Their vigilance in monitoring, their empathy in providing emotional support, and their expertise in medication administration are essential for saving lives and ensuring a patient’s recovery.”
“The focus should always be on treating the whole person,” explains Nurse Practitioner Sarah Jones, specializing in cardiac care. “We are not just treating a heart attack; we are treating a person who may be experiencing physical, emotional, and psychological distress.”
Nursing Care Plan For Patient With Myocardial Infarction
Conclusion: A Journey to Healing
Nursing care for a patient with myocardial infarction is a challenging yet immensely rewarding experience. Your role is not simply to administer care but to be a compassionate guide, offering support, knowledge, and empathy during a crucial time. By following the nursing care plan, you are instrumental in helping patients navigate this challenging health journey and emerge with a renewed sense of hope and strength. Remember, your dedication makes a profound difference in their lives. Continue to be a beacon of compassion, a guiding light on their path to healing.





