Imagine the joy of welcoming a newborn into the world, but the journey to that moment takes an unexpected turn, leading to a Cesarean section. While this surgical delivery is a common and safe procedure, it requires a specific and meticulous approach to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby. This is where the expertise and dedication of nurses come in, crafting personalized care plans tailored to the mother’s individual needs.

Image: studylib.net
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of nursing care plans for cesarean section, exploring the various aspects that contribute to the mother’s recovery and the baby’s health. From the immediate post-operative period to the crucial phases of recovery, we will examine the essential components of nursing care, providing valuable insights for nurses, patients, and anyone interested in understanding this critical aspect of healthcare.
Understanding Cesarean Section and Nursing Care
What is a Cesarean Section?
A Cesarean section, also known as a C-section, is a surgical procedure where a baby is delivered through an incision in the mother’s abdomen and uterus. This method is often chosen when a vaginal delivery is deemed unsafe for the mother or the baby, due to factors like fetal distress, placental abruption, breech presentation, or medical conditions.
Why are Nursing Care Plans Essential?
Nursing care plans are crucial for mothers who have undergone a Cesarean section for several reasons. They:
- Tailor care to individual needs: Each woman’s recovery journey is unique, and the care plan reflects her specific medical history, surgical complications, pain tolerance, and other factors.
- Promote optimal recovery: The plan guides nurses in providing the right interventions, from pain management and wound care to education and emotional support, ensuring a smoother recovery.
- Identify potential complications: Nurses are trained to monitor for signs of complications, such as infection, bleeding, or blood clots, and alert medical professionals promptly.
- Empower the patient: By understanding the care plan, mothers can actively participate in their recovery, ask questions, and express their concerns, fostering a collaborative approach to healthcare.
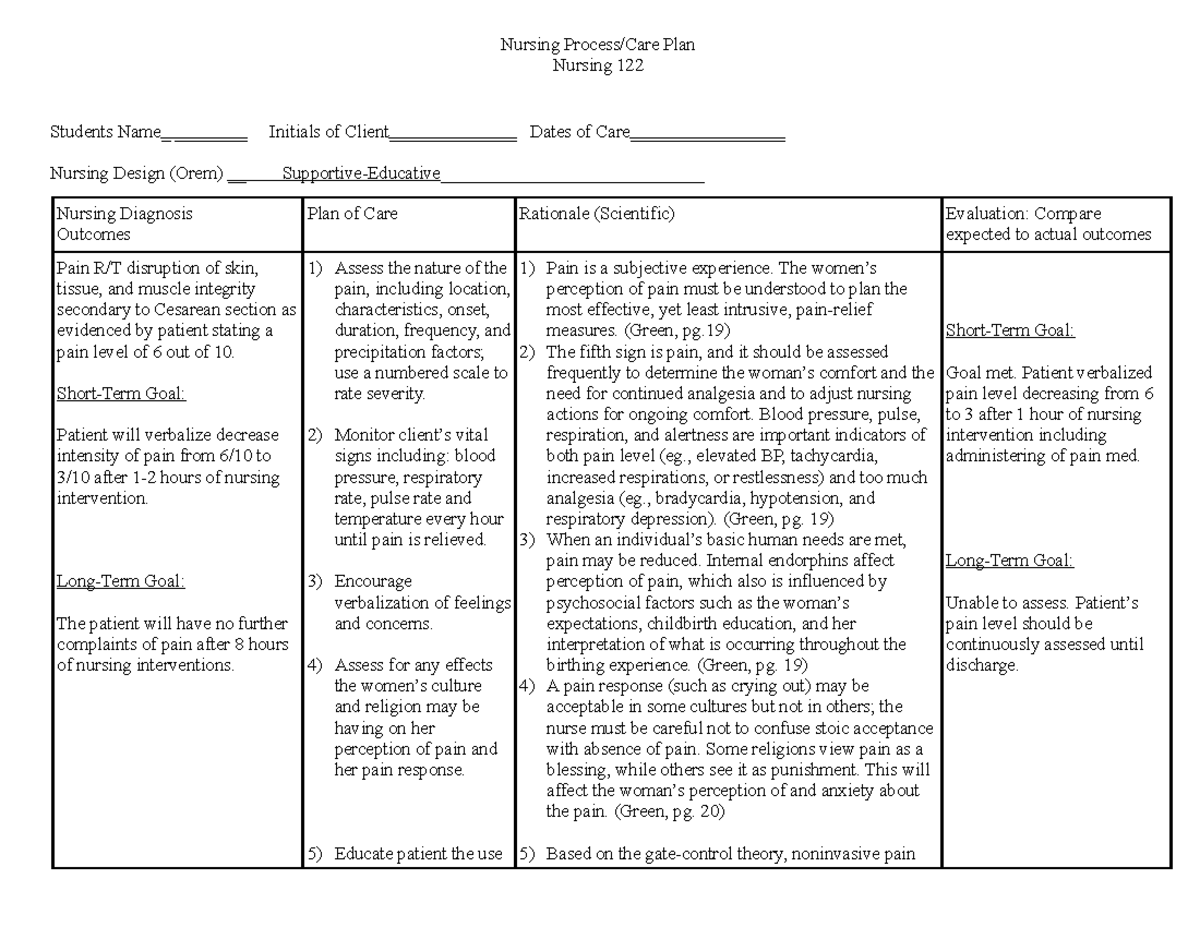
Image: www.studocu.com
The Nursing Care Plan: Key Elements
Assessment: The Foundation of Care
The nursing care plan begins with a thorough assessment, conducted shortly after the surgery. Nurses gather vital information about the mother’s physical and emotional state, including:
- Vital signs: Temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure are monitored to establish a baseline and detect any abnormalities.
- Pain level: Pain assessment is paramount to ensure adequate pain management, using a validated pain scale to gauge intensity and location.
- Wound status: Nurses meticulously examine the incision site, noting any signs of bleeding, redness, swelling, or drainage.
- Urinary output: Monitoring urine volume is essential to assess kidney function, as anesthesia and surgery can temporarily affect fluid balance.
- Gastrointestinal status: Nurses check for bowel sounds and assess the mother’s ability to pass gas, indicating normal bowel function.
- Emotional well-being: Cesarean section can be an emotionally challenging experience, and nurses are trained to provide emotional support and address anxieties.
Diagnosis: Identifying Nursing Concerns
Based on the assessment findings, nurses identify potential nursing diagnoses, which are health problems that nurses can treat independently. These diagnoses may include:
- Acute pain: Post-operative pain is a common concern, and nurses implement strategies to manage it effectively.
- Risk for infection: Cesarean section creates an open wound, making the mother susceptible to infection, so nurses prioritize wound care and hygiene.
- Impaired mobility: Pain and incisional discomfort can limit mobility, leading to complications like blood clots and respiratory issues. Nurses encourage early ambulation and provide assistance when needed.
- Deficient knowledge: New mothers may have limited understanding of post-operative care and recovery. Nurses provide clear and concise education, answering questions and addressing concerns.
- Anxiety: The surgical experience can induce anxiety, particularly for first-time mothers. Nurses offer emotional support, reassurance, and resources to alleviate anxiety.
Planning: Designing a Personalized Care Plan
The nursing care plan outlines specific interventions designed to address the identified nursing diagnoses. Key components include:
- Pain Management: Nurses provide pain relief through a variety of methods, such as medication (oral, IV, or epidural), positioning, and cold therapy.
- Wound Care: Nurses meticulously clean and dress the incision site, monitoring for signs of infection. They also provide education on wound care at home.
- Ambulation and Activity: Nurses encourage early ambulation to prevent blood clots and promote lung expansion. They guide mothers on safe movement and provide assistance when needed.
- Fluid and Nutrition: Adequate hydration and nourishment are vital for recovery. Nurses monitor intake and output, and they assist with feeding if necessary.
- Emotional Support: Nurses provide compassionate care, answering questions, listening to concerns, and offering emotional support and resources.
- Education: Nurses educate mothers on wound care, pain management, signs of complications, rest and activity, medication regimens, and follow-up appointments.
Implementation: Putting the Plan into Action
The nursing care plan is implemented through a series of interventions, including:
- Administering medications: Pain relievers, antibiotics, and other medications are given as prescribed.
- Providing wound care: Wound dressings are changed, and the incision is assessed for signs of infection.
- Encouraging ambulation: Nurses assist mothers in getting out of bed and moving around safely.
- Monitoring vital signs: Regular monitoring of temperature, pulse, respiration, and blood pressure ensures early detection of complications.
- Teaching and counseling: Nurses provide education on post-operative care, breast-feeding, and other topics.
- Documentation: Nurses meticulously document all assessments, interventions, and patient responses in the medical record.
Evaluation: Assessing Progress and Adjusting the Plan
Throughout the recovery journey, nurses continuously evaluate the mother’s progress, reassessing her needs and adjusting the care plan as needed. For example, if pain levels are not adequately controlled, the pain management plan may be revised. If the mother’s wound heals well and her mobility improves, the focus may shift to promoting breastfeeding or other post-operative care needs.
Specific Nursing Interventions: Addressing Common Post-Cesarean Section Concerns
Pain Management
Post-operative pain is a significant concern for mothers after a Cesarean section. Nurses employ various strategies to provide effective pain relief, including:
- Pharmacological interventions: Pain medications, such as analgesics, narcotics, and anti-inflammatories, are administered orally, intravenously, or via epidural infusion.
- Non-pharmacological methods: Nurses incorporate non-pharmacological pain relief techniques, such as positioning, cold therapy, and relaxation exercises.
- Assessing pain levels: Nurses regularly assess pain levels using a validated pain scale, ensuring that pain is adequately controlled.
Wound Care
Wound care is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing. Nurses follow specific guidelines and protocols to ensure optimal wound management, including:
- Cleaning and dressing: The incision site is cleaned with sterile solutions and dressed with appropriate wound dressings.
- Monitoring for complications: Nurses carefully watch for signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, warmth, drainage, or fever.
- Education: Nurses educate mothers on proper wound care at home, including how to keep the incision clean, dry, and protected.
Promoting Mobility
Early ambulation is encouraged after Cesarean section to prevent blood clots, improve lung function, and promote overall recovery. Nurses play a vital role in facilitating this process:
- Assisting with ambulation: Nurses assist mothers in getting out of bed and moving around safely, providing support and guidance.
- Encouraging movement: Nurses encourage mothers to move around as tolerated, reminding them of the benefits of activity.
- Addressing mobility issues: Nurses address any mobility limitations caused by pain or discomfort, providing pain relief or adapted strategies to ensure safe movement.
Promoting Bowel Function
Surgery and anesthesia can disrupt bowel function, leading to constipation. Nurses implement strategies to promote regular bowel movements:
- Dietary advice: Nurses recommend high-fiber foods, plenty of fluids, and avoiding constipation-inducing foods.
- Stool softeners: Stool softeners or laxatives may be prescribed to aid in bowel regularity.
- Encouraging activity: Gentle activity, such as walking or light exercise, can stimulate bowel motility.
Promoting Breastfeeding
Mothers who choose to breastfeed can begin immediately after Cesarean section, with proper support. Nurses help facilitate successful breastfeeding:
- Lactation support: Nurses provide lactation support, teaching proper latch techniques and positioning for successful breastfeeding.
- Addressing challenges: Nurses address any challenges mothers may face, such as nipple pain, latch difficulties, or low milk supply.
- Encouraging skin-to-skin contact: Nurses encourage early skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby, promoting bonding and successful breastfeeding.
Addressing Emotional Needs
Cesarean section can be an emotionally challenging experience, and nurses provide compassionate support to address the mother’s emotional needs:
- Empathy and understanding: Nurses approach mothers with empathy and understanding, acknowledging the emotional impact of surgery.
- Active listening: Nurses actively listen to mothers’ concerns and anxieties, providing a safe space for them to express themselves.
- Emotional resources: Nurses provide information and resources to address emotional challenges, such as anxiety, stress, or postpartum depression.
Nursing Care Plans For Cesarean Section
Conclusion: A Holistic Approach to Cesarean Section Care
Nursing care plans for Cesarean section are essential for ensuring a safe and comfortable recovery for mothers and their newborns. By employing a holistic approach that encompasses pain management, wound care, mobility promotion, breastfeeding support, and emotional well-being, nurses contribute significantly to the mother’s journey back to health and the establishment of a strong mother-infant bond. The next time you encounter a woman recovering from a Cesarean section, remember the intricate and compassionate care that lies at the heart of her well-being.





