Ever found yourself stranded with a dead car battery or a malfunctioning headlight, only to discover that the culprit could be a blown fuse? Navigating the intricate world of fuse boxes can be daunting, especially for car owners who aren’t familiar with the inner workings of their vehicle. The 2007 Kia Sedona, with its spacious interior and practical minivan design, is no exception. Understanding the fuse box diagram can be the difference between frustration and a quick fix, empowering drivers to address minor electrical issues with confidence.
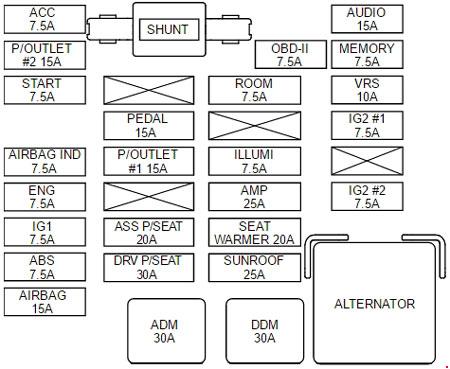
Image: www.autogenius.info
This comprehensive guide aims to demystify the 2007 Kia Sedona fuse box, providing a clear and detailed explanation of its location, layout, and functionality. We’ll delve into the different types of fuses, their purpose and how to replace them safely, equipping you with the knowledge to handle minor electrical troubles with ease. Ready to gain a deeper understanding of your trusty Sedona and become a more confident DIYer? Buckle up – let’s start exploring the world of fuses.
Location, Location, Location: Where to Find the Fuse Box
The 2007 Kia Sedona boasts two fuse boxes strategically placed for easy access: the Under-hood Fuse Box and the Interior Fuse Box.
Under-hood Fuse Box
This fuse box is usually located under the hood, near the battery, and often protected by a plastic cover. To access it, simply lift the hood and locate the box. The 2007 Kia Sedona’s under-hood fuse box is a central hub for numerous electrical components, controlling power supply to crucial systems like the engine, headlights, and cooling fan.
Interior Fuse Box
The interior fuse box is typically found on the driver’s side of the dashboard, often within the glove compartment or behind a small, removable panel. This fuse box primarily manages the electrical systems within the cabin, controlling components like the power windows, radio, and dashboard lights.

Image: turnnerkimikosays.blogspot.com
Decoding the Mystery: Understanding Fuse Types and Their Functions
Before delving into the specifics of the 2007 Kia Sedona fuse box, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental differences between the fuse types commonly used in automotive applications:
Blade Fuses
The most ubiquitous type of fuse, blade fuses are compact and easy to replace. They feature a thin metal strip that melts when excessive current passes through it, interrupting the electrical circuit and protecting components from damage. Blade fuses come in various amperage ratings, each designed to handle a specific amount of current. A higher amperage rating signifies a greater load capacity.
Mini Fuses
Similar to blade fuses, mini fuses are also quite common. However, they are smaller in size, making them ideal for tight spaces. Mini fuses also employ a thin metal strip that melts under high current, protecting components from overloads.
Fuseable Links
Unlike replaceable fuses, fuseable links are permanently integrated with the wiring harness. These thicker wires feature a thin section that melts under excessive current, breaking the circuit. Fuseable links are often used for high-current applications, such as the engine starter circuit.
Relays
Relays are electromechanical switches that control high-power circuits using a low-current signal. They are often found in conjunction with fuses within a fuse box. Relays can activate multiple components simultaneously or provide a higher current path than a standard fuse would allow.
Navigating the 2007 Kia Sedona Fuse Box Diagram: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let’s dive into the 2007 Kia Sedona fuse box diagram itself. The diagram serves as a roadmap, detailing the location of each fuse and its corresponding function. It’s essentially a blueprint for understanding the electrical system of your vehicle. To effectively use the diagram, here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Find Your Diagram: Locate the 2007 Kia Sedona fuse box diagram. You can often find it in your owner’s manual, online on Kia’s website, or in a repair manual. Be sure to confirm that you’re using the correct diagram for your year and model of Sedona.
2. Identify the Fuse Box: Determine whether you are working with the under-hood fuse box or the interior fuse box. The diagram will clearly indicate which fuse box it refers to.
3. Locate the Fuse: The diagram will have a numbered grid layout representing the fuse boxes. Each grid number corresponds to a specific fuse location within the box. Identify the fuse number associated with the electrical component you need to address.
4. Match the Amperage: Each fuse is designated by a specific amperage rating. The diagram will indicate the correct amperage rating for each fuse. It is crucial to replace a blown fuse with one of the same amperage rating. Using a fuse with too high of an amperage rating can lead to damage to components due to overload. A fuse with too low of an amperage rating will constantly blow due to insufficient current capacity.
5. Replace the Fuse: Carefully remove the blown fuse using a fuse puller or pliers. Insert the new fuse of the same amperage rating into the empty slot. Ensure the fuse is properly seated to guarantee adequate contact.
Safety First: Precautions for Working with Fuses
Working with electrical components requires caution. Always adhere to the following safety precautions to minimize the risk of electrical shock or injury:
1. Disconnect the Battery: Disconnect the negative terminal of the car battery before working on any electrical components. This prevents any possibility of accidental electrical shock or short circuits.
2. Avoid Contact with Live Wires: Never touch live wires or connectors, as this can lead to severe electrical shock. Always use gloves or tools to handle electrical components.
3. Use Proper Tools: Only use tools designed for fuse removal and installation. Using inappropriate tools can damage the fuse box or create a hazard.
4. Follow the Diagram: Always refer to the fuse box diagram for accurate fuse identification and replacement. Never replace fuses blindly. Incorrect fuse placement can lead to malfunctions and damage to electrical components.
5. Consult a Professional: If you are unsure about any aspect of the fuse box, or if you encounter persistent electrical problems, it’s always best to consult a qualified automotive technician.
Fuse Box Trouble: Common Symptoms and Troubleshooting Tips
A blown fuse can often be the culprit behind common electrical problems you might encounter in your 2007 Kia Sedona. Here are some common symptoms and troubleshooting tips for addressing these issues:
No Lights/Dim Lights
If your headlights, taillights, or instrument panel lights are not working properly, check the fuses responsible for these circuits. Be sure to check all relevant fuses, not just the ones on the diagram that seem directly related. Sometimes, a blown fuse in another circuit can affect related components.
Power Window Malfunction
If your power windows are not working, check the fuse that controls the window circuit. The fuse box diagram will specify the fuse related to the affected window, or even the entire power window system.
Radio Issues
A blown fuse can cause a radio to malfunction or stop working altogether. Check the radio’s fuse on the fuse box diagram, ensuring you replace it with the correct amperage.
Intermittent Electrical Problems
If you experience intermittent electrical issues, such as flickering lights or temporary power loss, check all fuses related to the affected circuits. It’s possible that a fuse is on its way out, intermittently interrupting the circuit.
Beyond the Fuse Box: Understanding Electrical System Basics
Understanding the basic principles of automotive electrical systems can further enhance your DIY skills and help you pinpoint electrical troubleshooting issues more effectively.
1. The Battery: The battery serves as the heart of the electrical system. It stores electrical energy and provides power to the starter motor, lights, and other components when the engine is off.
2. The Alternator: The alternator generates electrical power while the engine is running. It replenishes the battery and powers all electrical components when the engine is running.
3. The Starter Motor: The starter motor uses power from the battery to rotate the engine, allowing it to start.
4. The Wiring Harness: The wiring harness acts as a network, connecting the battery, alternator, starter motor, and all other electrical components. It provides a path for electrical current to flow throughout the vehicle.
2007 Kia Sedona Fuse Box Diagram
Empower Your DIY Skills: Mastering the 2007 Kia Sedona Fuse Box
By understanding the layout, functionality, and significance of the 2007 Kia Sedona fuse box, you are empowered to handle minor electrical troubles and become a more confident DIYer. Armed with the knowledge of the various fuse types, amperage ratings, and fuse location, you can confidently diagnose and address common electrical issues, empowering you to make repairs without the need for professional intervention. Remember to always prioritize safety, consult the fuse box diagram for accuracy, and be cautious when working with electrical components. With this guide as your compass, you’re well on your way to conquering those electrical puzzles that your 2007 Kia Sedona might throw your way.





