Picture this: you’re driving down a scenic highway, the engine purring smoothly, propelling your car effortlessly. You might not realize it, but a crucial factor behind this seamless experience is the mean effective pressure (MEP) of your engine’s Otto cycle. This invisible force, measured in pressure units like Pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi), acts as the driving force behind the pistons, dictating the efficiency and power output of your vehicle.
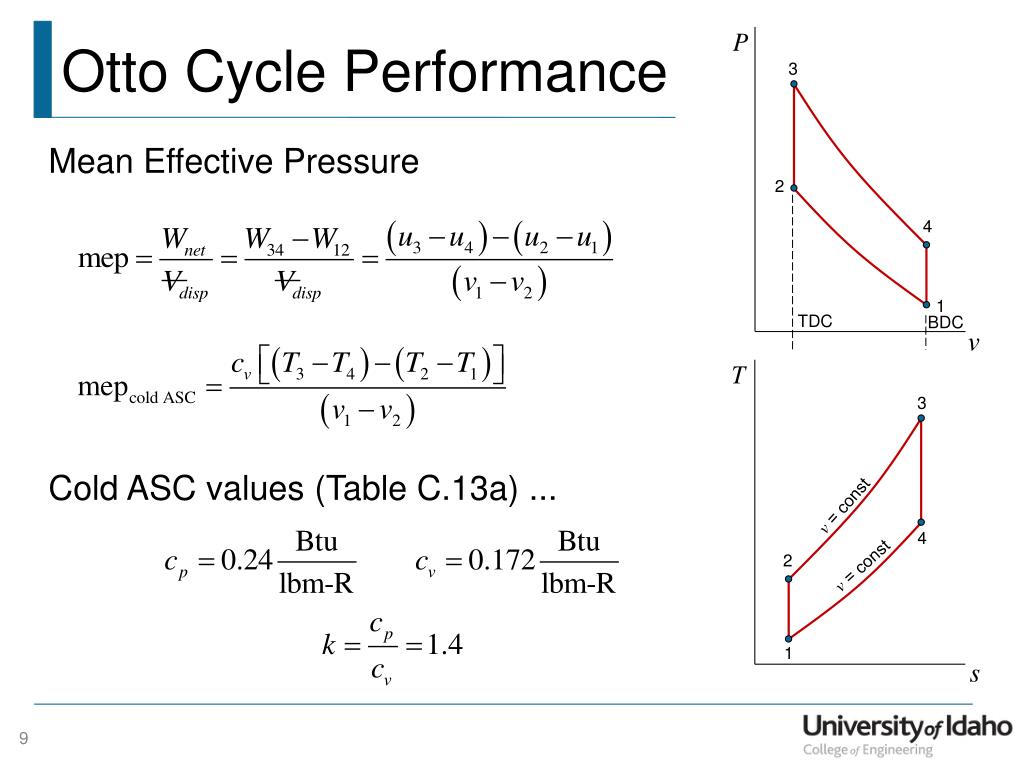
Image: www.slideserve.com
The Otto cycle, the fundamental thermodynamic cycle employed in most gasoline engines, is a sequence of four strokes – intake, compression, power, and exhaust – that transform fuel energy into mechanical work. Mean effective pressure, a crucial parameter within this cycle, plays a pivotal role in determining the engine’s ability to convert fuel into motion. This article delves into the intricacies of mean effective pressure, exploring its definition, calculation, significance, and optimization techniques.
Understanding Mean Effective Pressure
The mean effective pressure (MEP) represents the average pressure exerted on the piston during the power stroke of an Otto cycle. It is a theoretical concept that effectively captures the overall pressure driving the piston, irrespective of the variations in pressure during the different stages of the cycle. This pressure is measured in units like Pascals (Pa) or pounds per square inch (psi).
The concept is rooted in the fundamental principle of work being done by a force over a distance. The MEP allows engineers to simplify the complex pressure variations within the cylinder into a single, representative value that significantly simplifies the calculation of power output. Moreover, it provides a crucial metric for comparing the performance of different engines, offering valuable insights into their efficiency and power capabilities.
Defining Mean Effective Pressure
In essence, mean effective pressure reflects the hypothetical constant pressure, uniformly distributed across the piston throughout the power stroke, that would generate the same amount of work as the actual varying pressure within the cylinder. It is a crucial parameter in engine design, enabling engineers to optimize the power output and efficiency of their engines.
The MEP is not a directly measurable value; rather, it is a calculated metric derived from other parameters, such as the cylinder pressure, volume, and crankshaft angle. The formula used to calculate MEP is:
MEP = (Net Work Done / Displacement of Cylinder)
Factors Affecting Mean Effective Pressure
Several factors influence the mean effective pressure of an Otto cycle, directly affecting the engine’s performance. Some key factors include:
- Compression Ratio: A higher compression ratio leads to a higher MEP, resulting in greater power output.
- Intake and Exhaust System Design: Improved intake and exhaust systems, facilitating better air intake and exhaust gas expulsion, can increase MEP, boosting efficiency.
- Fuel-Air Mixture: The stoichiometry of the fuel-air mixture plays a crucial role. A well-balanced mixture, ensuring complete combustion, results in higher MEP and better engine efficiency.
- Engine Speed: MEP generally increases with rising engine speed, translating to more power output.
- Spark Timing: Proper spark timing optimizes combustion, leading to higher MEP and improved engine performance.
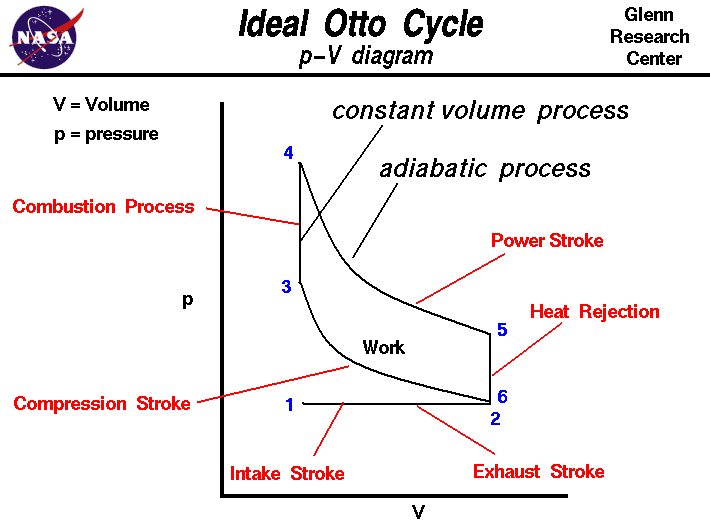
Image: lilinguas.com
Optimizing Mean Effective Pressure
Optimizing the MEP of an engine is a constant endeavor for engineers and researchers. The pursuit of higher MEP translates to increased power output, improved efficiency, and reduced emissions.
Several strategies are employed to elevate MEP, including:
- Advanced Engine Designs: Modern engine designs incorporating features like turbochargers, superchargers, and variable valve timing, can significantly increase MEP, enhancing power output and fuel efficiency.
- Advanced Combustion Technologies: Innovative combustion strategies, such as direct injection and lean-burn techniques, aim to optimize the combustion process, leading to higher MEP and lower emissions.
- Efficient Exhaust System: Optimized exhaust systems, facilitating efficient exhaust gas evacuation, can enhance the MEP by reducing back pressure and promoting better scavenging of the combustion chamber.
- Fuel Additives: Specific fuel additives can enhance combustion process efficiency, ultimately increasing the MEP and improving engine performance. However, it is crucial to use approved and recommended additives to avoid detrimental effects on engine components.
Tips and Expert Advice for Optimizing MEP
Here are some practical tips and expert advice for maximizing the mean effective pressure of your engine:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure your engine is well-maintained with timely oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug replacements to ensure optimum performance. A clean engine can significantly contribute to higher MEP.
- High-Octane Fuel: Using high-octane fuel can improve combustion efficiency, particularly in engines with high compression ratios. This can lead to higher MEP and better power delivery.
- Performance Modifications: Consider engine modifications like a cold air intake or exhaust system upgrades that can increase airflow and boost MEP, improving overall engine power.
- Driving Habits: Adopt smooth and efficient driving habits. Aggressive acceleration and harsh braking can lead to fuel inefficiency and a decrease in MEP.
Remember, consulting with a qualified mechanic or automotive specialist is always recommended when exploring engine modifications, as they can advise on the best options for your vehicle and ensure compatibility with its design.
FAQ about Mean Effective Pressure
Q: What is the relationship between mean effective pressure and engine power?
A: Mean effective pressure and engine power are directly related. A higher MEP translates to greater power output. The engine power is calculated using the formula:
Power = (MEP × Displacement × Engine Speed) / (2π × 60)
Q: How does mean effective pressure affect engine efficiency?
A: Increased MEP generally corresponds to improved engine efficiency. A higher MEP signifies more efficient conversion of fuel energy into mechanical work, resulting in better fuel economy.
Q: What are some common applications of mean effective pressure calculations in the automotive industry?
A: The concept of MEP finds applications in various aspects of the automotive industry, including:
- Engine Design and Development: MEP calculations aid in optimizing engine performance and efficiency during the design phase.
- Performance Tuning: Understanding MEP is essential for tuning engines to achieve optimal power output and fuel efficiency.
- Comparing Engine Performance: MEP provides a standardized metric for comparing the performance of different engines.
- Emissions Control: MEP is a factor considered in optimizing engine performance while minimizing emissions.
Mean Effective Pressure Of Otto Cycle
Conclusion
The mean effective pressure of an Otto cycle is a pivotal concept in understanding engine performance and power output. It represents the average pressure driving the piston during the power stroke, directly impacting the engine’s efficiency and fuel economy. Optimization of MEP through advancements in engine designs, combustion technologies, and driving habits remains a key area of focus for the automotive industry, aiming to improve power output while reducing environmental impact.
Are you interested in learning more about Otto Cycle and its applications in engineering?





