Ever wondered what makes you, you? The answer lies in your genes, the blueprints of life. But have you ever considered the intricate dance between DNA and RNA, the two key players in this genetic symphony? These molecules, found in every living cell, are responsible for everything from your eye color to your susceptibility to certain diseases. Delving into the world of DNA and RNA can seem complex, but understanding their differences is crucial to comprehending the fundamental mechanisms of life. This is where a DNA vs. RNA worksheet comes in handy, providing a clear roadmap to navigate the intricacies of these genetic giants.
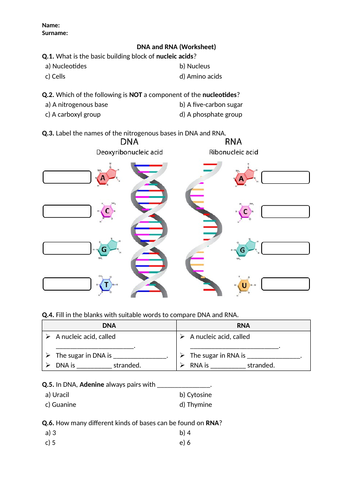
Image: www.tes.com
Imagine you’re a detective, investigating a crime. You find clues, analyzing fingerprints and DNA samples. This analysis helps you understand the event, just as studying DNA and RNA helps us understand how life functions. Today, we’ll analyze the clues in a DNA vs. RNA worksheet, revealing the secrets of these molecular marvels.
Unlocking the Secrets: DNA vs. RNA
Let’s begin by defining our players. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the primary blueprint of life, containing the genetic instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Think of DNA as a master plan, a set of detailed instructions for making every protein your body needs. RNA, or ribonucleic acid, is the versatile messenger that carries these instructions from DNA to the protein-building machinery in the cell. It’s like a copy of the master plan, taken to the construction site to guide the building process.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the differences between DNA and RNA, using the information on your DNA vs. RNA worksheet.
The Structural Differences: DNA vs. RNA
Imagine DNA as a twisted ladder, a double helix structure. Each side of the ladder is made of a sugar-phosphate backbone, with nitrogenous bases acting as the rungs. The four nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). These bases pair up in a specific way: A always bonds with T, and G always bonds with C. This specific pairing is crucial for ensuring accurate replication of DNA.
RNA, on the other hand, has a single-stranded structure, more like a straight chain. Its sugar-phosphate backbone also has nitrogenous bases, but instead of thymine, RNA uses uracil (U). So, in RNA, A pairs with U, and G with C. This structural difference affects how these molecules function.
The Functional Differences: DNA vs. RNA
DNA’s primary role is to store genetic information, acting as a blueprint for life. It resides in the nucleus of the cell, carefully guarded within chromosomes. When a cell needs to create a protein, DNA’s instructions are copied onto a messenger RNA (mRNA). This mRNA molecule then travels to the ribosome, the protein-building machinery of the cell.
There are different types of RNA, each with a specialized function. mRNA, mentioned earlier, carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosome. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a structural component of the ribosome, and transfer RNA (tRNA) brings the amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, to the ribosome.
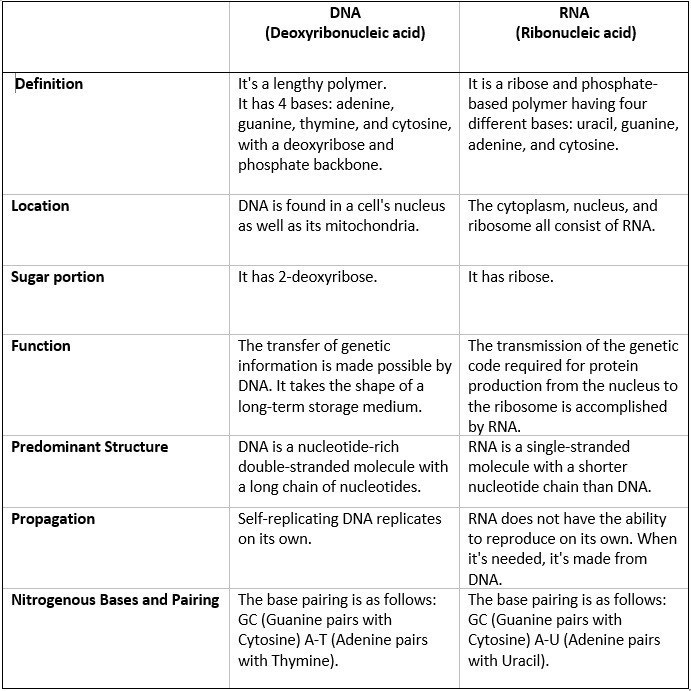
Image: inspiritvr.com
The Worksheet as a Tool for Learning
Using a DNA vs. RNA worksheet can greatly enhance your understanding of these molecules. It allows you to identify key differences between DNA and RNA in a structured format. You’ll be able to see side-by-side comparisons of their structure, composition, function, and location within the cell. By analyzing the information provided, you can solidify your understanding of these biochemical giants.
Tips for Maximizing Your Understanding
To make the most of your DNA vs. RNA worksheet, here’s a simple approach:
- Start with the Basics: Read the definitions and descriptions of DNA and RNA. Understand their roles as the blueprint and messenger of life.
- Focus on the Key Differences: Analyze the structure, composition, and function of each molecule. Note the key differences in their sugar-phosphate backbones, nitrogenous bases, and overall structure.
- Visualize the Processes: Try to visualize how DNA replicates and how RNA transcribes. Imagine the mRNA molecule traveling from the nucleus to the ribosome, carrying its genetic message.
- Connect the Concepts: Relate the information you learn to your understanding of protein synthesis. Understand how DNA, RNA, and proteins work together to build and maintain life.
FAQ: DNA vs. RNA
Here are some frequently asked questions about DNA and RNA:
- What is the difference between DNA and RNA in terms of their sugar components?
DNA contains deoxyribose sugar, while RNA contains ribose sugar.
- Which nitrogenous base is found in RNA but not DNA?
Uracil, denoted by the letter U, is present in RNA but not DNA. In DNA, uracil is replaced by thymine (T).
- What is the main function of DNA?
DNA’s primary function is to store genetic information, carrying the blueprint for building and maintaining an organism.
- What are the different types of RNA?
There are three main types of RNA: mRNA (messenger RNA), rRNA (ribosomal RNA), and tRNA (transfer RNA).
- Is it possible for DNA and RNA to be converted into each other?
Yes, this process is known as reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptase, an enzyme, can copy RNA into DNA, a crucial step in viral replication and some laboratory techniques.
Dna Vs Rna Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion: The Dance of Life
The DNA vs. RNA worksheet is a valuable tool for understanding the fundamental building blocks of life. By analyzing their differences, you gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate processes that drive everything we experience. Remember, the next time you see a DNA model, visualize its complex structure and its role in the grand symphony of life. Think about the role RNA plays in carrying out DNA’s instructions, making life possible.
Are you interested in learning more about the fascinating world of DNA and RNA? If so, share your thoughts in the comments below!





