Imagine walking into a room full of strangers, each with their own unique story and health concerns. Your job is to quickly assess each person’s overall well-being, identifying potential issues and determining the best course of action. This is the daily reality for many medical professionals, and it’s a task that requires a systematic and thorough approach. Enter the “head-to-toe assessment,” a crucial tool in the medical world.

Image: www.studocu.com
A head-to-toe assessment is a comprehensive evaluation that examines a patient’s physical condition from head to toe. It’s a crucial part of routine physical examinations, emergency assessments, and ongoing patient care. A well-designed assessment script can streamline the process, ensuring no vital signs or symptoms are missed. This article will delve into the intricacies of head-to-toe assessment scripts, exploring their importance, components, and how they can be effectively utilized, providing you with a solid foundation for understanding this essential medical practice.
Understanding the Head-to-Toe Assessment Script
A head-to-toe assessment script is a structured document that outlines the steps involved in systematically evaluating a patient’s physical condition. It serves as a checklist, ensuring that the examiner covers all critical areas of the body, from the scalp to the toes. The most effective assessment scripts are comprehensive, adaptable, and easy to follow. They are designed to be used by medical professionals, from nurses and paramedics to doctors and physical therapists.
Key Benefits of Utilizing a Head-to-Toe Assessment Script
The benefits of implementing a head-to-toe assessment script are numerous:
- Streamlined Evaluation: The script serves as a consistent guide, ensuring that all relevant areas are examined in a logical order, leading to a more complete and accurate assessment.
- Increased Efficiency: By following the structured approach, health professionals can complete assessments more quickly and effectively, saving valuable time. This is especially critical in emergency situations.
- Reduced Errors: The checklist format minimizes the risk of overlooking details. The script serves as a safety net, enhancing the accuracy of the assessment and minimizing the potential for missed diagnoses.
- Improved Communication: The standardized script ensures consistency in communication between medical professionals. A clear and concise assessment report can help facilitate effective handoffs and improve patient care.
Components of a Head-to-Toe Assessment Script
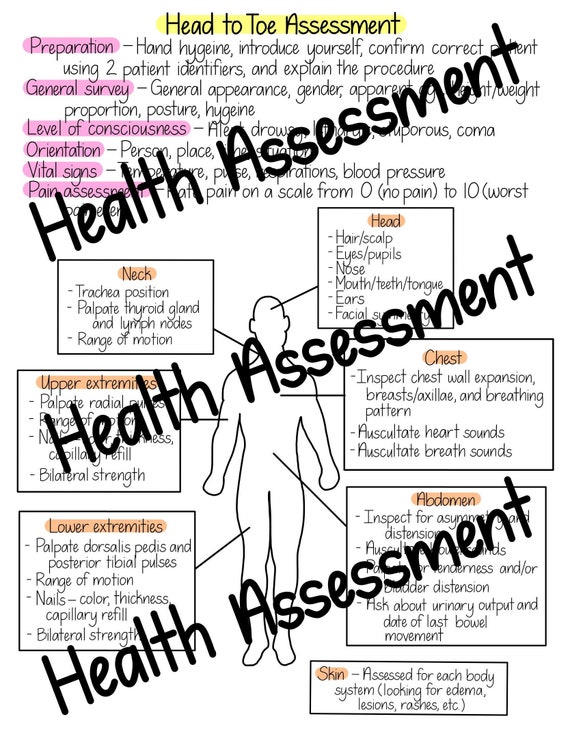
Image: www.myxxgirl.com
The Initial Assessment
A head-to-toe assessment script begins with initial observations and vital signs. These include:
- General Appearance: This encompasses the patient’s overall demeanor, including their level of consciousness, breathing effort, skin color, and posture.
- Vital Signs: These are the fundamental indicators of a patient’s health status. They include temperature, pulse, blood pressure, respirations, and, in some cases, oxygen saturation levels.
- Pain Assessment: Pain is subjective and highly individualized. The script should include a thorough and detailed assessment of any reported pain, considering its location, intensity, duration, and quality.
The Head and Neck
The assessment continues with a meticulous examination of the head and neck:
- Head: This involves inspecting the scalp for any lesions, parasites, or signs of trauma. It also includes examining the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth for any abnormalities or injuries.
- Neck: This involves assessing the neck’s range of motion, palpating the lymph nodes, and examining the jugular veins and carotid arteries.
The Respiratory System
Assessing the respiratory system is crucial for identifying potential lung issues:
- Chest: This includes observing breathing patterns, auscultating (listening) to lung sounds, and palpating the chest for any tenderness or abnormalities.
The Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system assessment includes examining the heart and blood vessels. This involves:
- Heart: This includes auscultating heart sounds for murmurs, gallops, or other abnormalities. Palpating the chest for thrills, which are vibrations generated by turbulent blood flow.
- Peripheral Vasculature: This includes checking for adequate blood flow in the extremities, palpating pulses, and assessing the appearance of the skin for signs of poor circulation.
The Gastrointestinal System
The gastrointestinal system assessment includes:
- Abdomen: This involves inspecting the abdomen for distention, scars, and masses, auscultating for bowel sounds, and palpating the abdomen for tenderness or masses.
The Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal assessment includes examining the bones, muscles, and joints:
- Musculoskeletal: This involves assessing the range of motion in each joint, palpating for tenderness, and examining the muscles for strength and atrophy.
The Neurological System
The neurological assessment includes a series of tests to evaluate the patient’s neurological function:
- Neurological: This assessment includes assessing the patient’s level of consciousness, orientation (time, place, person), memory, language, and motor function. It also involves testing reflexes, sensation, and coordination.
The Integumentary System
The integumentary system assessment includes examining the skin, hair, and nails:
- Skin: This assessment includes inspecting the skin for color changes, lesions, bruising, wounds, and signs of inflammation.
Creating a Head-to-Toe Assessment Script PDF
The creation of a head-to-toe assessment script is a collaborative effort. While different professionals have varying needs, here are some general guidelines.
Steps for Creating a High-Quality, Effective Script:
- Identify Target Audience: Define the specific professionals who will use the script. Are you targeting nurses, paramedics, doctors, or a specific specialty? This will help tailor the script’s content, complexity, and language.
- Choose a Structure: Develop a logical flow for the script. Consider the most efficient order for completing the assessment. Start with basic observations and vital signs and progress to more detailed examinations of different body systems.
- Define Assessment Categories: Break down the assessment into clear, concise sections. These could include categories like “General Appearance,” “Head and Neck,” “Respiratory System,” etc.
- List Essential Examination Steps: Detail the key areas to inspect, palpate, auscultate, or test for each section. Provide clear instructions and potential findings to look for.
- Include Space for Documentation: Provide readily accessible spaces for recording findings in a clear, structured format. This could include checklists for vital signs, spaces for notes, and sections for recording any further examination findings.
- Preview and Iterate: Have a group of professionals review and test the script in real-world settings. Gather feedback to ensure clarity, accuracy, and user-friendliness.
Tips and Expert Advice
Here are some tips from seasoned medical professionals for utilizing head-to-toe assessment scripts effectively:
- Practice Regularly: Use the script in simulated scenarios and hands-on practice to ensure proficiency and comfort with the assessment process.
- Adapt and Customize: Remember that a script is a guide, not a rigid formula. Adapt it as needed based on patient-specific factors and the available resources.
- Prioritize the Most Important Information: While comprehensive, the script should prioritize the essential data required to make a timely and appropriate assessment.
- Be Mindful of Patient Comfort: Always be respectful and informative. Explain the process to the patient and ensure their comfort throughout the assessment.
Head-to-Toe Assessment Script FAQs
Q: What types of professions can benefit from utilizing a head-to-toe assessment script?
A: A wide range of medical professionals benefit from using head-to-toe assessment scripts, including nurses, paramedics, doctors, physical therapists, and even some allied health practitioners.
Q: How often should a head-to-toe assessment script be used?
A: The frequency of using a head-to-toe assessment script varies depending on the patient’s condition and the healthcare setting. It’s typically performed during routine physical examinations, emergency assessments, and periodic evaluations in patients with chronic conditions.
Q: What is the difference between a physical exam and a head-to-toe assessment?
A: A physical exam is a broader term, encompassing various assessments, while a head-to-toe assessment is a more specific component of a physical exam. It focuses on systematically examining the entire body from head to toe.
Q: Are there any legal or ethical implications associated with using a head-to-toe assessment script?
A: Utilizing a head-to-toe assessment script is generally considered standard practice in many healthcare settings. However, it’s crucial to be familiar with relevant legal and ethical guidelines and ensure the script is aligned with professional standards and patient confidentiality.
Q: Where can I find templates or examples of head-to-toe assessment scripts?
A: You can find examples of head-to-toe assessment scripts online, in medical textbooks, and through professional organizations. Many healthcare institutions and departments may also have their own pre-designed scripts that are tailored to their specific needs.
Head To Toe Assessment Script Pdf
Conclusion
The head-to-toe assessment script is an invaluable tool for medical professionals. As we’ve discussed, a well-structured assessment script can significantly improve the efficiency, accuracy, and communication of patient assessments. By adopting a systematic approach, healthcare professionals gain valuable insights into a patient’s overall health, leading to improved diagnoses, treatment plans, and patient outcomes.
Are you interested in learning more about head-to-toe assessment scripts or medical assessment tools? Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Let’s continue learning and improving our understanding of this vital medical practice that contributes directly to patient care.





