My fascination with Roman numerals began during a visit to the Colosseum in Rome. As I stood among the ancient stones, I noticed the intricate carvings, bearing dates and inscriptions in this timeless system. It struck me then that these symbols, so simple yet powerful, had held the secrets of counting for centuries. I was captivated by the idea that a system so old could still hold a certain mystery and allure. This sparked a desire to delve deeper into the world of Roman numerals and explore their history, structure, and practical applications.

Image: www.pinterest.co.uk
Today, we often take for granted the Arabic numerals that form the foundation of our modern numerical system. However, the Roman numerals, with their unique system of letters and symbols, offer a glimpse into a different way of representing numbers. While Roman numerals may seem archaic, they continue to hold relevance in various aspects of our lives, from clock faces and chapter headings to architectural designs and even the naming of popes and monarchs.
Understanding Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, uses letters to represent numbers. Its simplicity lies in the use of seven basic symbols:
The Core Symbols
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| V | 5 |
| X | 10 |
| L | 50 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 500 |
| M | 1000 |
By combining these symbols, the Romans were able to represent numbers up to thousands. The system relies on the following rules:
Rules of Combination
- Repetition: Repeating a symbol up to three times multiplies its value. For example, III represents 3, XX represents 20, and CCC represents 300.
- Subtraction: Placing a smaller symbol to the left of a larger symbol subtracts its value. For example, IV represents 4 (5 – 1), IX represents 9 (10 – 1), and CM represents 900 (1000 – 100).
- Addition: A smaller symbol placed to the right of a larger symbol adds its value. For example, VI represents 6 (5 + 1), XV represents 15 (10 + 5), and MC represents 1100 (1000 + 100).
It’s important to note that some combinations are not allowed. For instance, you cannot have more than three repeated symbols in a row (like IIII) and you cannot have two subtraction symbols in a row. Instead, you would use the additive principle. For example, instead of writing IIII, you would write IV, or instead of writing IIXX, you would write XVIII.
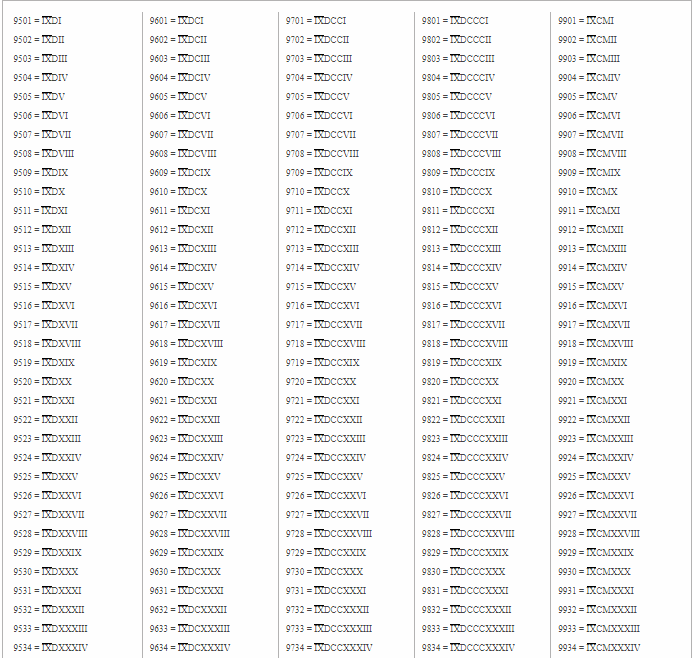
Image: romansnumerals.com
Roman Numerals 1 to 10,000: A Comprehensive Guide
Armed with these rules, we can now delve into constructing Roman numerals from 1 to 10,000. Understanding the pattern and logic is key to mastering this ancient numerical system. Here’s a breakdown:
1 to 10
- I
- II
- III
- IV
- V
- VI
- VII
- VIII
- IX
- X
11 to 20
- XI
- XII
- XIII
- XIV
- XV
- XVI
- XVII
- XVIII
- XIX
- XX
21 to 30
- XXI
- XXII
- XXIII
- XXIV
- XXV
- XXVI
- XXVII
- XXVIII
- XXIX
- XXX
You can apply the same logic to represent numbers from 31 to 100, 101 to 200, and so on. To represent numbers above 1000, simply repeat the ‘M’ symbol. For example, MM represents 2000, MMM represents 3000, and so on.
Numerals 1001 to 10,000
To represent numbers between 1001 and 10,000, you use the symbol ‘M’. You can repeat up to three times for 2000, 3000, and 4000. For any number between these, you can use the symbols for 1 to 999, adding them to the ‘M’. For example, 1001 would be represented as ‘MI’, 1002 would be ‘MII’, and 1009 would be ‘MIX’. This pattern continues throughout the range until you reach 10,000. To represent 10,000, you would use the symbol for 1,000 followed by a symbol for 10,000, which is denoted by a bar over the symbol. So, the Roman numeral for 10,000 would be ‘M̄’.
Roman Numerals in Today’s World
While the use of Roman numerals has declined with the widespread adoption of the Arabic numeral system, they remain prominent in various contexts. They are commonly seen on clock faces, where they denote the hours, adding a touch of classic elegance. They are also used in chapter headings of books and other publications, providing a clear visual distinction between sections. Architects and designers still incorporate Roman numerals in their work, often to create a sense of grandeur and historical charm.
Examples of modern use of Roman numerals
- Clock faces: XII, III, VI, IX
- Chapter headings: Chapter I, Chapter II, Chapter III
- Architectural designs: On buildings, monuments, and other structures to convey historical significance or grandeur
- Monarchs and popes: King George VI, Queen Elizabeth II, Pope Francis
- Film and television: Titles of films and television shows, often to create a sense of timelessness and intrigue.
Tips for Working with Roman Numerals
Here are a few tips to help you master Roman numerals and confidently use them in various situations:
1. Memorize the Basic Symbols
Mastering the seven basic symbols, their values, and combinations is critical. Once you have a firm grasp of these fundamentals, you’ll be able to decipher any Roman numeral.
2. Practice, Practice, Practice
Convert Arabic numbers to Roman numerals and vice versa, and gradually increase the complexity. This consistent practice will solidify your understanding of the rules and improve your speed and accuracy.
3. Utilize Online Tools and Resources
Various online resources, such as Roman numeral converters and learning websites, can be invaluable for exploring the system and finding answers to specific questions. They provide an easy way to test your knowledge and deepen your understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why are Roman numerals still used today?
Roman numerals are still used today because of their historical connection, aesthetic appeal, and their presence in specific contexts such as clock faces, chapter headings, and architectural designs.
Q: How do you read Roman numerals?
Roman numerals are read from left to right. The values of the symbols are added together unless a smaller value symbol appears to the left of a larger value symbol, in which case it is subtracted.
Q: Can I use Roman numerals for everyday calculations?
While it’s possible to perform calculations with Roman numerals, the Arabic numeral system is more practical for everyday calculations and modern mathematics. Roman numerals are primarily used for symbolic purposes or to represent dates and numbers in specific scenarios.
Q: Are there any rules for using Roman numerals?
Yes, there are certain rules for using Roman numerals. The most important rules involve the repetition of symbols, the placement of smaller symbols, and the allowed combinations. Understanding these rules will ensure you write and read Roman numerals correctly.
Roman Numerals 1 To 10 000
Conclusion
Roman numerals, with their distinct historical roots and enduring presence in various contexts, continue to captivate and intrigue us. From their ancient origins to their use in modern society, these symbols offer a window into a different numerical world, reminding us of the enduring legacy of the Roman civilization. Understanding their system and being able to navigate their structure is a valuable skill, adding another dimension to our knowledge of numbers.
Are you curious to learn more about Roman numerals or to explore other historical numerical systems? Share your thoughts and any questions you may have in the comments section below.





