Have you ever wondered why a straw in a glass of water appears to be bent at the surface? Or why a magnifying glass can make objects seem larger? The answer lies in a fascinating phenomenon called light refraction. This bending of light as it passes from one medium to another is at the heart of how lenses work, and it’s a concept that’s explored in numerous science worksheets.

Image: niko-bogspotwatson.blogspot.com
If you’re looking for answers to a light refraction and lenses worksheet, you’ve come to the right place. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of light refraction, exploring the concepts behind it, the types of lenses, and how they work. We’ll also provide tips and insights to help you navigate your worksheet with confidence.
Understanding Light Refraction and Lenses
Light refraction is a fundamental concept in physics that plays a crucial role in our understanding of how light interacts with matter. When light travels from one medium to another—say, from air to water—its speed changes. This change in speed causes the light to bend, a phenomenon known as refraction. The amount of bending depends on the angle at which the light strikes the surface and the refractive indices of the two media.
Lenses harness the power of light refraction to manipulate light rays. They are typically made of transparent materials like glass or plastic, carefully shaped to focus or spread out light. There are two primary types of lenses:
- Converging lenses (convex lenses): These lenses are thicker in the middle than at the edges, causing parallel light rays to converge at a focal point.
- Diverging lenses (concave lenses): These lenses are thinner in the middle than at the edges, causing parallel light rays to diverge as if they were coming from a focal point behind the lens.
Exploring the Wonders of Light Refraction and Lenses
Light refraction and lenses have a wide range of applications, impacting our daily lives in countless ways. From the eyeglasses we wear to correct our vision to the powerful telescopes that allow us to explore the depths of space, lenses play a vital role in shaping our world.
The Science Behind the Bend
To truly understand why light bends when it enters a different medium, we need to think about the nature of light itself. Light travels as waves, and the speed of these waves changes when they move from one medium to another. This change in speed causes the wave to bend, leading to the phenomenon we call refraction.
Imagine a swimmer approaching a beach at an angle. If they continue swimming at the same angle, they’ll reach the shore at a different point than if they’d approached straight on. The same principle applies to light, as it experiences a similar change in direction when transitioning between media.
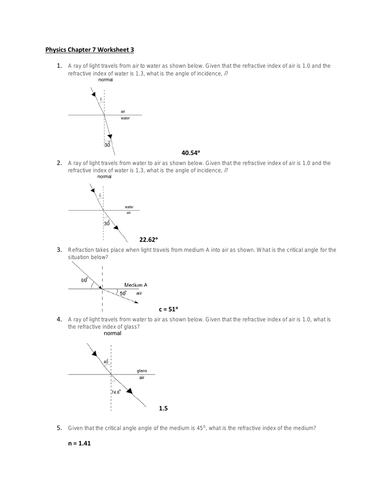
Image: www.tes.com
Lenses in Action: Shaping Our World
Lenses are indispensable tools in various fields, utilizing the principle of light refraction to perform specific tasks. Here are some key examples:
- Eyeglasses and contact lenses: These lenses correct refractive errors like nearsightedness and farsightedness by focusing light correctly on the retina.
- Microscopes: Microscopes use lenses to magnify tiny objects, revealing details invisible to the naked eye.
- Telescopes: Telescopes employ lenses to gather and focus light from distant objects, enhancing our ability to observe celestial bodies.
- Cameras: Camera lenses control the amount of light entering the camera and focus it onto the sensor to capture images.
- Projectors: Projectors use lenses to project images onto a screen, allowing us to share presentations and movies.
Tips for Mastering Light Refraction and Lenses
Tackling a light refraction and lenses worksheet can be a rewarding experience, helping you to grasp the fundamentals of how light behaves. Here are some valuable tips to ensure success:
- Visualize the Concepts: Draw diagrams to help you understand how light rays bend through lenses. This visual representation can enhance your comprehension.
- Practice with Real-World Examples: Look at objects through different lenses—a magnifying glass, eyeglasses, or even a water-filled glass—to visualize the effects of refraction.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Ask Questions: If you encounter a concept you don’t understand, ask your teacher or classmates for clarification.
FAQs
Here are some frequently asked questions about light refraction and lenses:
Q: Why does a straw in water appear bent?
A: The straw appears bent because light from the straw travels through air and then enters water. The change in medium causes the light to refract, making the straw seem bent at the surface of the water.
Q: What is the difference between a converging lens and a diverging lens?
A: A converging lens is thicker in the middle, causing parallel light rays to converge at a focal point. A diverging lens is thinner in the middle, causing parallel light rays to diverge as if they were coming from a focal point behind the lens.
Q: How do eyeglasses help correct vision?
A: Eyeglasses use lenses to correct refractive errors like nearsightedness (myopia) and farsightedness (hyperopia). A nearsighted person has trouble seeing distant objects because light focuses in front of the retina, and a converging lens helps to redirect the light to focus on the retina. A farsighted person has trouble seeing near objects because light focuses behind the retina, and a diverging lens helps to spread out the light so it focuses on the retina.
Light Refraction And Lenses Worksheet Answers Pdf
Conclusion
Light refraction and lenses are fascinating topics that reveal the wonders of the world around us. As you explore the concepts of light bending and lens properties, remember that you’re delving into a field that has shaped human history and continues to drive innovation in technology and scientific discovery.
Are you interested in learning more about the amazing world of light refraction and lenses?





