Imagine a scenario: a patient lies in a hospital bed, their skin pale and clammy, their pulse weak and rapid. Their breathing is shallow, and they complain of dizziness and lightheadedness. This patient is experiencing the consequences of ineffective tissue perfusion, a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when blood flow to tissues is compromised. This is where the nursing diagnosis of “risk for ineffective tissue perfusion” comes into play, a crucial tool for nurses to identify and intervene early, potentially preventing serious complications.
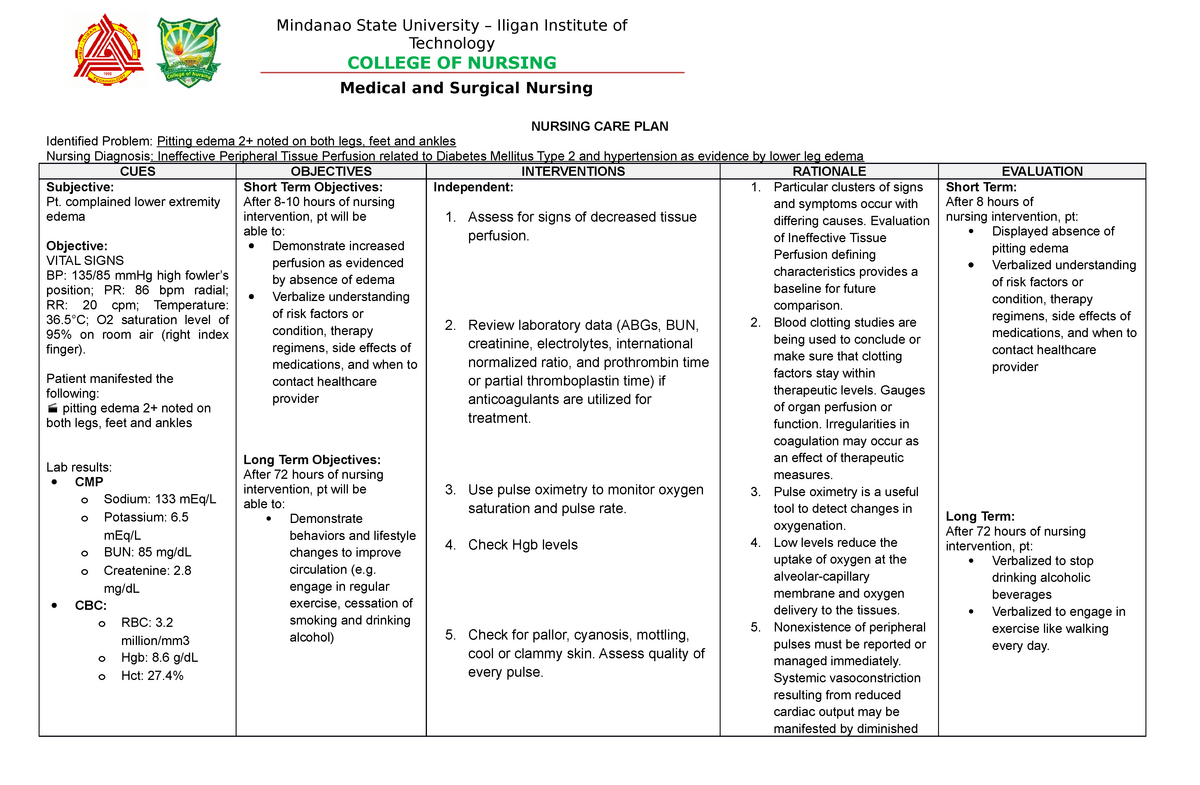
Image: www.studocu.com
This article delves into the intricacies of “risk for ineffective tissue perfusion” as a nursing diagnosis, exploring its causes, symptoms, nursing interventions, and how it impacts patient care. We will unravel the complexities of tissue perfusion, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of this critical diagnosis and its implications in the healthcare setting.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Tissue Perfusion
Before diving into the complexities of the nursing diagnosis, let’s define the core concept: tissue perfusion. In essence, it refers to the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to target tissues while simultaneously removing waste products, a delicate balance essential for cellular function and survival.
The Vital Role of the Cardiovascular System
The circulatory system, our intricate network of blood vessels, plays the starring role in this process. The heart, a tireless pump, propels blood through arteries, delivering oxygenated blood and essential nutrients to tissues. Meanwhile, veins act as return routes, transporting deoxygenated blood and waste products back to the heart and lungs.
Factors that Influence Tissue Perfusion
Tissue perfusion is a dynamic process influenced by a multitude of factors, including:
- Heart Function: A strong, healthy heart is crucial for efficient blood pumping.
- Blood Vessel Integrity: Healthy arteries and veins, free from blockages or narrowing, ensure smooth blood flow.
- Blood Volume: Adequate blood volume is necessary to maintain sufficient pressure for tissue perfusion.
- Blood Viscosity: The thickness of blood influences its flow rate.
- Oxygen Content: The amount of oxygen carried by the blood directly impacts tissue oxygenation.
- Metabolic Demand: Tissues with elevated metabolic activity, such as muscles during exercise, require increased blood flow.

Image: es.scribd.com
Recognizing the Risk: Understanding the Nursing Diagnosis “Risk for Ineffective Tissue Perfusion”
The nursing diagnosis “risk for ineffective tissue perfusion” is a predictive judgment that indicates a patient’s susceptibility to impaired blood flow to tissues. This diagnosis is not a direct assessment of current tissue perfusion but a proactive measure to identify individuals at risk of developing this complication, allowing nurses to implement preventative measures.
Why is this Diagnosis Important?
Early identification of risk factors for ineffective tissue perfusion is critical because compromised blood flow can lead to:
- Cellular Ischemia: Lack of oxygen and nutrients can cause cell damage and death.
- Tissue Necrosis: Severe ischemia can lead to tissue death and gangrene.
- Organ Failure: Sustained inadequate perfusion can damage organs, leading to organ dysfunction or failure.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Impaired Tissue Perfusion
While the risk for ineffective tissue perfusion is a prediction, certain signs and symptoms can indicate a potential problem:
- Changes in Skin Color: Pale, cyanotic (bluish), or mottled skin can hint at reduced blood flow.
- Altered Temperature: Cool or cold extremities are a common sign of poor perfusion.
- Edema: Swelling in the extremities can occur due to fluid buildup.
- Altered Sensation: Numbness, tingling, or pain in extremities can indicate nerve damage due to ischemia.
- Altered Pulse: Weak or absent pulses in the extremities may signal compromised blood flow.
Risk Factors That Lead to Ineffective Tissue Perfusion
Nurses must closely assess patient demographics, medical history, and current conditions to identify individuals at risk for ineffective tissue perfusion. Here are some common risk factors:
Medical Conditions
- Cardiovascular Disease: Conditions like heart failure, coronary artery disease, or arrhythmias severely affect heart function and blood flow.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing or blockage of arteries in the legs or feet restricts blood flow to extremities.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can damage blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of PAD and other circulatory problems.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls, leading to reduced perfusion.
- Anemia: Reduced red blood cell count or low hemoglobin levels limit oxygen-carrying capacity, potentially impacting tissue oxygenation.
- Hypovolemia: Decreased blood volume, often due to dehydration or bleeding, lowers blood pressure and impairs tissue perfusion.
Lifestyle Factors
- Smoking: Nicotine constricts blood vessels, impairing blood flow and increasing the risk of PAD.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity weakens the cardiovascular system and increases the risk of blood clots.
- Obesity: Excess weight strains the heart and can lead to high blood pressure and other circulatory problems.
- High Cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to atherosclerosis, narrowing of arteries, and reduced perfusion.
Medications and Procedures
- Medications: Certain medications, such as vasodilators, can lower blood pressure and potentially affect tissue perfusion.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgery can increase the risk of blood clots, particularly in the legs, potentially leading to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism.
- Trauma: Severe trauma, like a fractured bone or extensive injuries, can disrupt blood flow and increase the risk of complications.
Nursing Interventions for At-Risk Patients
When a nurse identifies a patient at risk for ineffective tissue perfusion, a personalized care plan is developed to address those risk factors. Nursing interventions vary depending on the patient’s individual needs and contributing factors. However, common interventions include:
Monitoring and Assessment
- Vital Signs: Regularly monitoring blood pressure, pulse, and respiratory rate provides a baseline for assessing perfusion.
- Skin Assessment: Examining skin color, temperature, and capillary refill time provides vital clues about peripheral circulation.
- Pain Assessment: Pain in the extremities can be a sign of ischemia and should be thoroughly assessed.
- Edema: Monitoring for any swelling in the extremities can indicate fluid buildup and potential perfusion issues.
Medications and Treatments
- Antiplatelets or Anticoagulants: These medications help prevent blood clot formation, reducing the risk of blockages.
- Vasodilators: By widening blood vessels, these medications improve blood flow.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplying additional oxygen can improve tissue oxygenation, particularly in cases of low oxygen levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for improving circulation and reducing the risk of PAD.
- Healthy Diet: A diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol can benefit cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of atherosclerosis.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity strengthens the heart and improves circulation.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight reduces strain on the heart and improves overall circulation.
Patient Education and Support
- Educate Patients: Patients need to understand their specific risk factors and the importance of lifestyle modifications.
- Provide Support: Encouragement and support can empower patients to make healthy choices and manage their conditions effectively.
- Promptly Report Changes: Encourage patients to report any changes in their condition or symptoms immediately.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Effective nursing interventions are crucial in preventing the progression of ineffective tissue perfusion. Early identification of risk factors and prompt implementation of preventative measures can significantly minimize the risk of serious complications.
Collaborative Approach
Nurses work collaboratively with other healthcare professionals, such as physicians, pharmacists, and physical therapists, to develop comprehensive care plans. This interdisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the patient’s care are addressed.
Risk For Ineffective Tissue Perfusion Nursing Diagnosis
Continuous Evaluation and Adjustments
The nursing care plan is not static; it’s continually evaluated and adjusted based on the patient’s response to interventions. Patients’ conditions can change, requiring modifications to the care plan to ensure optimal outcomes.
This informative journey into the world of “risk for ineffective tissue perfusion” as a nursing diagnosis has highlighted the importance of early identification, comprehensive assessment, and tailored interventions in preventing this potentially life-threatening condition. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing the signs and symptoms, and effectively implementing nursing interventions, nurses play a crucial role in promoting patient safety and improving outcomes.
Continue to explore resources, share your experiences, and contribute to the ongoing advancement of nursing knowledge and practice. Together, we can enhance patient care and ensure the best possible outcomes for those at risk for ineffective tissue perfusion.





